In trigonometry, circular functions are also referred to as trigonometric functions. The definition of these functions in its simplest form is that it exhibits a close relationship between sides and angles of a triangle. Also known as trigonometric ratios, they are designated by cosecant, secant, cotangent, tangent, cosine and sine.
- Integration Formula
- Formula of Trigonometry
- Trigonometric Ratios
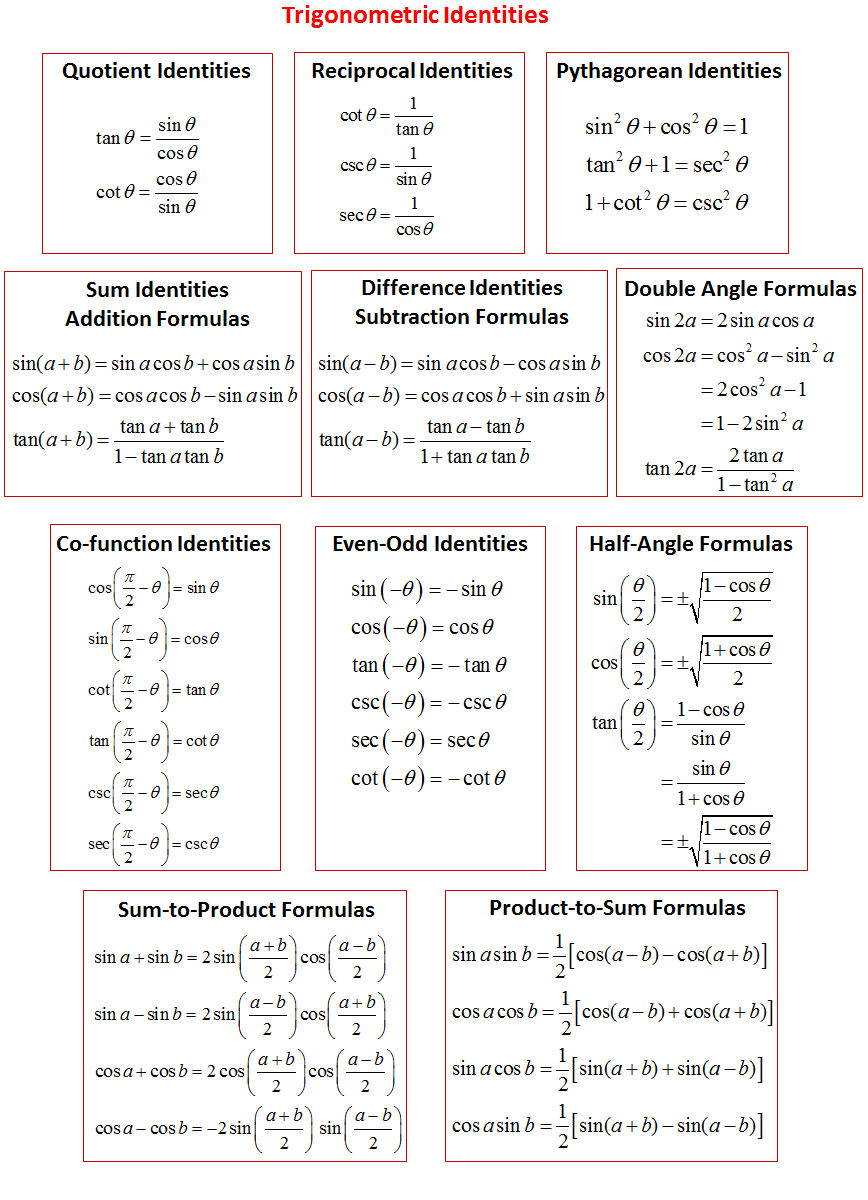
- Trig Identities
- What are Trigonometric derivatives
- Heights and distance
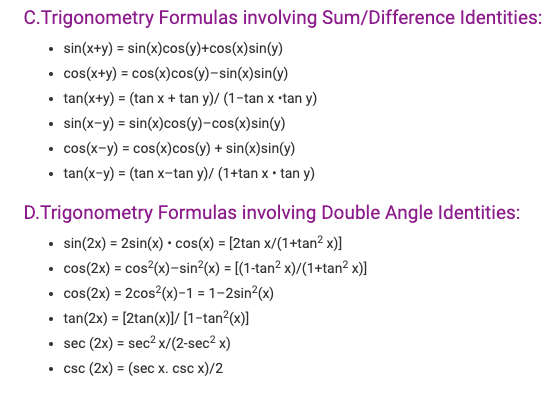
- Trigonometry formula Involving Sum Difference Product Identities
- Pythagorean Theorem
- Differentiation Formula
- Basic Trig Identities
Trigonometric Functions with Angles
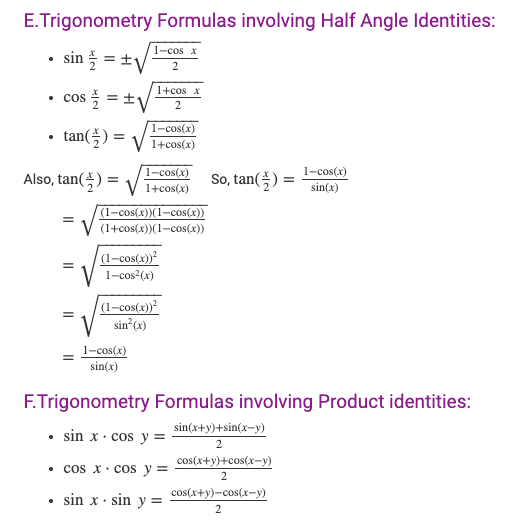
Any student learning these functions should understand that there are a number of trigonometric identities and formulas. The formulas establish relation between these functions.
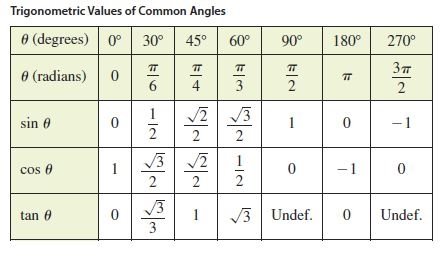
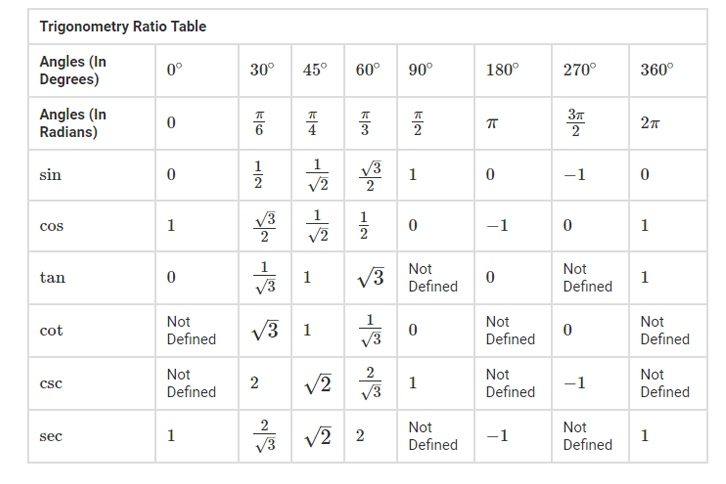
Trig Functions Table
The primary classification of trigonometric functions, includes the angles of tangent, cosine and sine. From these primary functions it is possible to derive three functions that are designated as cosecant, secant, and cotangent.
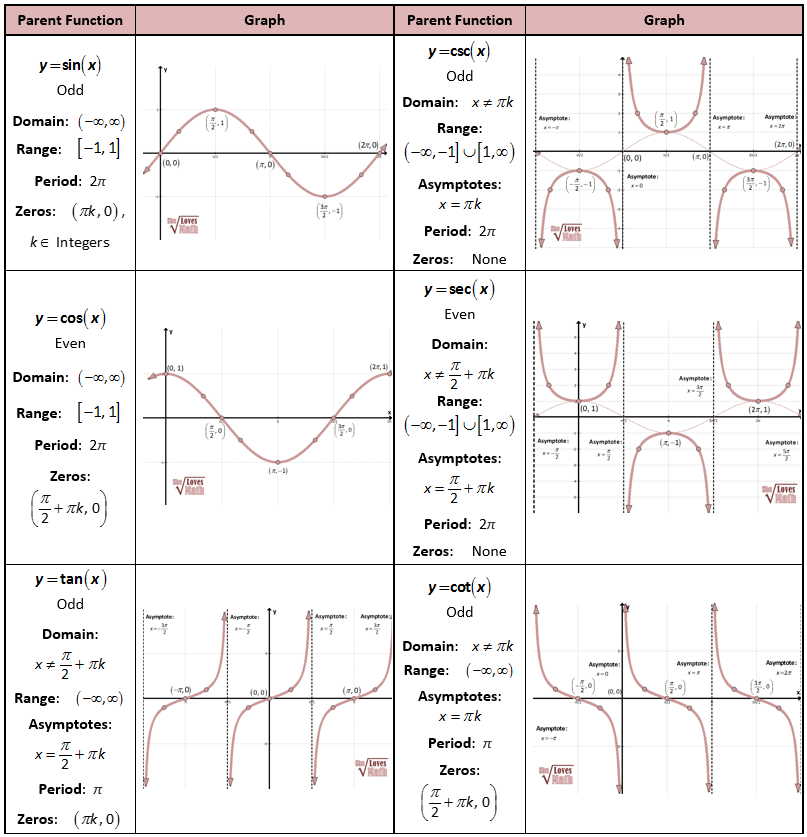
Trigonometric Functions with Graphs
The above diagram can explain the three trigonometric primary functions.
List of Trigonometric Functions
List of additional trigonometric functions include secant, cosecant, and cotangent. These functions are also established from the primary functions, like sine, cos and tan. It should be noted that the reciprocal of tan, cos, and sin are known as cotangent (cot), secant (sec), and cosecant (csc), respectively.
Trigonometric Functions Formula
The formula for some trigonometric functions is given below. They are:
The ratio between the length of an opposite side to that of the hypotenuse is known as, the sine function of an angle. The sin value should be Sin a= Opposite/Hypotenuse=CB/CA.
The cos function formula can be explained as the ratio of the length of the adjacent side to the length of hypotenuse. The cos function can be derived from the above reference diagram as
Cos a = Adjacent/Hypotenuse = AB/CA.
The tan function formula is defined as the ratio of the length of the opposite side of the right-angled triangle to that of the adjacent side. The student should note that the tan function can be exhibited in terms of sine and cos as their ratio. Hence, the tan function will be derived as Tan a = Opposite/Adjacent = CB/BA. Further, tan can be written in terms of sine and cos as Tan a = sina/cosa.
Additional functions are represented through formulas; they are:
Cot a = 1/ (tan a) = Adjacent/Opposite = BA/CB
Cosec a = 1/ (sin a) = Hypotenuse/Opposite = CA/CB
Sec a = 1/ (cos a) = Hypotenuse/Adjacent = CA/AB
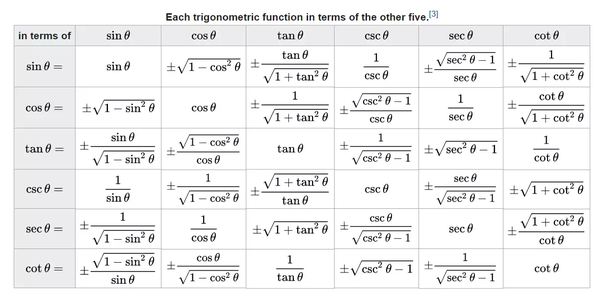
There are few inverse trigonometric functions. Here, the inverse of cosecant, secant, cotangent, tangent, cosine and sine, are known as arc cosecant, arc secant, arc cotangent, arc tangent, arc cosine, and arc sine respectively.
Trigonometry Formula
FAQs related to trigonometric functions with formulas
- What are trigonometric functions?
A: Trigonometric functions are mathematical functions that relate the angles of a right triangle to the ratios of the lengths of its sides. The most commonly used trigonometric functions are sine, cosine, and tangent.
2. What is the formula for sine?
A: The formula for sine is: sin(theta) = opposite/hypotenuse
3. What is the formula for cosine?
A: The formula for cosine is: cos(theta) = adjacent/hypotenuse
4: What is the formula for tangent?
A: The formula for tangent is: tan(theta) = opposite/adjacent
5. What is the reciprocal of sine?
A: The reciprocal of sine is cosecant. The formula for cosecant is: csc(theta) = hypotenuse/opposite
6. What is the reciprocal of cosine?
A: The reciprocal of cosine is secant. The formula for secant is: sec(theta) = hypotenuse/adjacent
7. What is the reciprocal of tangent?
A: The reciprocal of tangent is cotangent. The formula for cotangent is: cot(theta) = adjacent/opposite
8. What is the Pythagorean identity?
A: The Pythagorean identity states that for any angle theta in a right triangle, the following equation holds: sin^2(theta) + cos^2(theta) = 1
9. What is the double-angle identity for sine?
A: The double-angle identity for sine is: sin(2theta) = 2sin(theta)cos(theta)
10. What is the double-angle identity for cosine?
A: The double-angle identity for cosine is: cos(2theta) = cos^2(theta) – sin^2(theta)
11. What is the half-angle identity for sine?
A: The half-angle identity for sine is: sin(theta/2) = ±sqrt[(1-cos(theta))/2]
12. What is the half-angle identity for cosine?
A: The half-angle identity for cosine is: cos(theta/2) = ±sqrt[(1+cos(theta))/2]
13. What is the sum and difference formula for sine?
A: The sum and difference formula for sine is: sin(A ± B) = sin(A)cos(B) ± cos(A)sin(B)
14. What is the sum and difference formula for cosine?
A: The sum and difference formula for cosine is: cos(A ± B) = cos(A)cos(B) ∓ sin(A)sin(B)
15. What is the product-to-sum formula?
A: The product-to-sum formula is: sin(A)sin(B) = [cos(A – B) – cos(A + B)]/2
16. What is the sum-to-product formula?
A: The sum-to-product formula is: cos(A) + cos(B) = 2cos[(A + B)/2]cos[(A – B)/2]





Good job
How or what would be the formula to find out :
B=0.9143, find B?
Please help!!! I’m at a loss!